The IT management maturity matrix: a technical framework for scaling operations
In this article
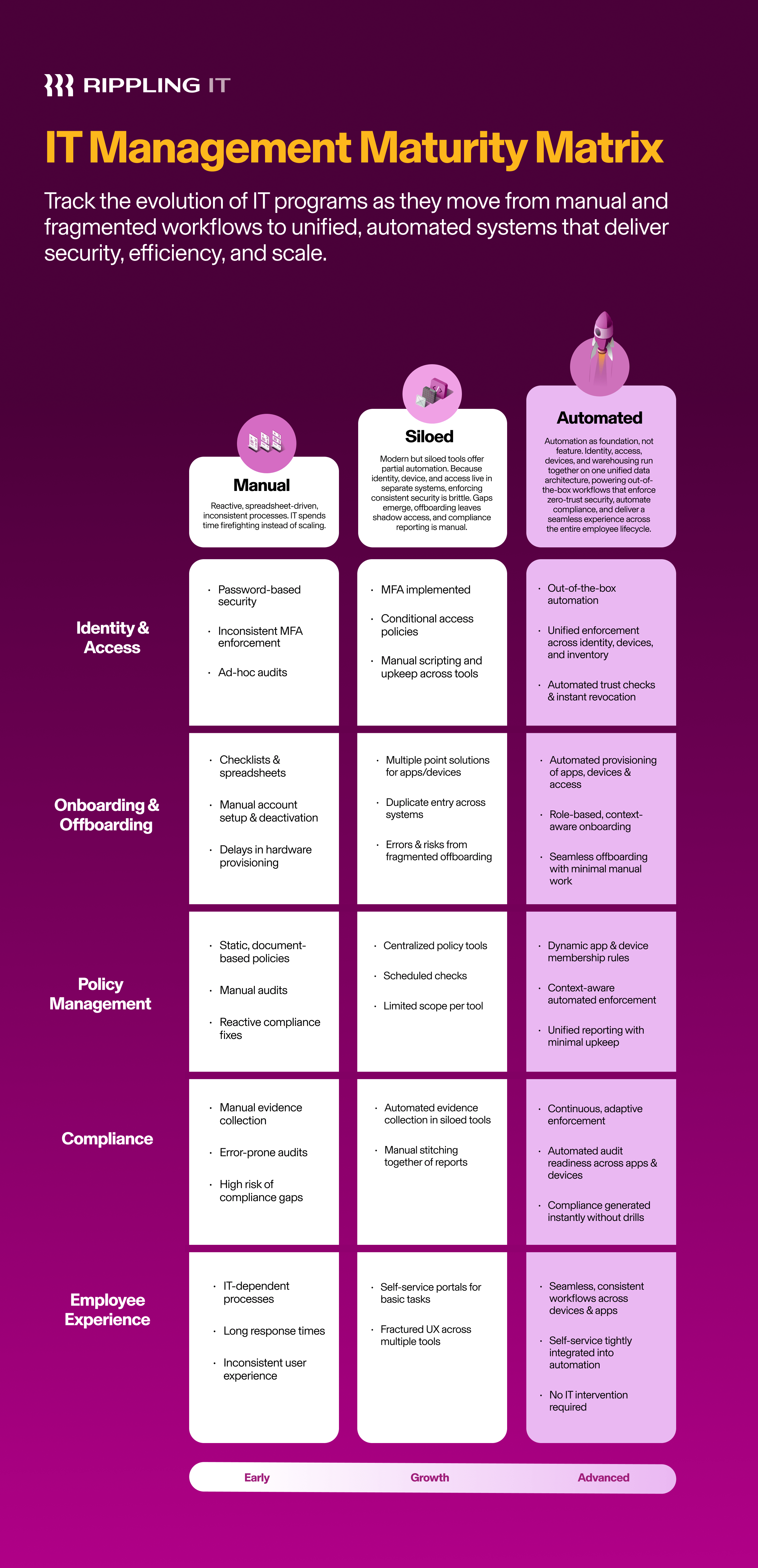
IT operations tend to travel along a linear maturity progression across five critical domains:
Identity & Access
Onboarding & Offboarding
Policy Management
Compliance
End-User Experience
Your team may not be operating at the same stage for each of those domains, but by and large, the transition from one stage to the next isn’t random. It follows predictable patterns driven by the fundamental tension between operational complexity and the mechanisms available to coordinate that complexity.
This framework maps the patterns that accompany one of three maturity stages: Manual, Siloed Point Solutions, and End-to-End Automation. More than a marginal shift, each stage represents a fundamentally different approach to managing a given domain of your IT infrastructure.
Our hope is that this maturity matrix provides a roadmap for understanding where your organization currently operates and the steps necessary to advance.
Read on for a detailed explanation of each section of the matrix and the three stages of maturity for each practice.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
As a foundational layer of IT/security architecture, how organizations authenticate users, authorize access, and manage credentials directly determines their security posture, incident response capabilities, and compliance readiness.
Manual: Decentralized state management
Manual IAM operates without centralized identity providers or programmatic access controls. Authorization state exists in spreadsheets, wikis, and institutional knowledge. Each application maintains independent user stores with no mechanism for synchronization.
Key characteristics:
Password-based authentication with inconsistent MFA implementation
Per-application account provisioning requiring O(U×S) operations for U users across S systems
Ad-hoc security audits triggered by compliance deadlines rather than continuous monitoring
No centralized session management or revocation capabilities
System limitations:
Former employee accounts persist due to incomplete manual deprovisioning
Permission drift occurs as users accumulate privileges through additive-only operations
Audit preparation requires reconstructing authorization state from multiple partial sources
Siloed point solutions: Partial consolidation with integration overhead
Organizations adopt MDM platforms and identity providers but operate them as discrete systems requiring custom integration and ongoing maintenance.
Key characteristics:
MFA and SSO implemented for subset of applications
Conditional access policies with manual rule configuration
Periodic security reviews using exported data
Identity provider deployment with limited automation and integration gaps
System limitations:
Each point solution manages its own scope, creating coordination overhead
Scripting requirements for cross-system operations introduce fragility
Security policies require manual translation across different platforms
Offboarding still requires manual orchestration across multiple consoles
End-to-end automation: Unified identity fabric
Identity, devices, and access management converge on a single platform with native data integration, enabling programmatic policy enforcement and automated lifecycle management.
Key characteristics:
Fully automated identity lifecycle from provisioning to deprovisioning
Zero-trust architecture with continuous authentication and authorization
Context-aware access controls based on real-time device trust, location, and behavioral analytics
Automated policy enforcement across all systems with instant revocation capabilities
The transition to end-to-end automation replaces multiple integrated systems with a single platform where identity, device, and access management share a common data layer. This native integration removes the need for middleware, synchronization scripts, and cross-system coordination between disparate tools, as well as the administrative overhead and technical debt inherent to the manual stage.
Onboarding and offboarding
Employee lifecycle management maturity reflects the organization's ability to coordinate atomic operations across distributed systems.
Manual: Sequential operations with human coordination
New employee provisioning requires coordinating across multiple people and systems through email, spreadsheets, and checklist-driven workflows.
Key characteristics:
Checklist-based tracking with manual execution
Asynchronous provisioning across independent systems
Device procurement and configuration as separate manual processes
Offboarding requiring manual access revocation across each system individually
System limitations:
New hire provisioning exhibits high latency due to sequential bottlenecks
Configuration drift occurs as each device receives manual setup
Incomplete offboarding creates security exposure when manual processes inevitably miss systems
Siloed point solutions: Automation with integration gaps
Organizations deploy provisioning tools and device management platforms but must manually orchestrate across system boundaries.
Key characteristics:
Automated provisioning for subset of applications
MDM platforms for device deployment with partial automation
Approval workflows within individual systems
Each point solution managing its own user lifecycle with manual coordination between them
System limitations:
Multiple access tools produce coordination overhead during role transitions
New hire onboarding still requires duplicate data entry across systems
Offboarding requires logging into multiple consoles to revoke access, track hardware, and update records
End-to-end automation: Unified lifecycle orchestration
Employee lifecycle events trigger coordinated workflows across identity, devices, and access management from a single source of truth.
Key characteristics:
Automated, role-aware provisioning of apps, devices, and credentials
Pre-built onboarding touchpoints delivering logistics, benefits, and instructions before day one
Scheduled offboarding with automatic access revocation at specified time
Device tracking, data archiving, and compliance reporting integrated into lifecycle workflows
End-to-end automation emerges when lifecycle events in one domain automatically cascade across systems, removing the manual handoffs of spreadsheet-driven processes and the brittle integrations required when HR, IAM, and MDM systems operate independently.
Policy management
Policy management maturity measures the gap between documented requirements and enforced reality: the degree to which written security standards translate into automated, verifiable controls.
Manual: Static documentation sans enforcement
Security policies exist as documents that require human interpretation and manual implementation.
Key characteristics:
Policy documents stored in static file formats
Manual interpretation of requirements by system administrators
Periodic audit-driven compliance verification
No programmatic enforcement—policies are recommendations rather than controls
System limitations:
Policy documents update but implementations lag
Security requirements depend on administrator execution, creating inconsistent security posture
Policy violations persist undetected until audits reveal gaps
Siloed point solutions: Centralized management with disjointed scope
Policy tools provide centralized management but each platform enforces only its own domain.
Key characteristics:
Centralized policy management tools with scheduled compliance checks
Automated enforcement within each tool's scope
Manual coordination required for cross-platform policies
Each point solution managing its own policy lifecycle
System limitations:
Cross-platform policies require manual translation and enforcement across multiple systems
Policy updates in one system don't automatically propagate to others
Compliance reporting requires stitching together data from multiple sources
End-to-end automation: Dynamic, context-aware policy enforcement
Policies span applications and devices with dynamic enforcement based on real-time context.
Key characteristics:
Custom policies built on unified user and device data
Dynamic policy application based on role, location, device status, and other attributes
Automated enforcement that applies immediately as context changes
Unified compliance reporting with continuous monitoring
End-to-end automation migrates the organization from document-based policies and fragmented enforcement tools to infrastructure built on a common data layer. Policies leverage attributes spanning identity, location, device status, and application context to enforce sophisticated rules across all systems simultaneously.
Compliance
Compliance maturity reflects the organization's ability to demonstrate security controls continuously and proactively rather than in response to external audits.
Manual: Reactive evidence collection
Compliance operates as an annual event requiring manual evidence gathering when auditors request it.
Key characteristics:
Manual evidence collection from multiple systems
Spreadsheet-based compliance tracking
High latency between security events and evidence generation
Error-prone audits with high risk of gaps
System limitations:
Compliance preparation diverts substantial engineering resources
Audit preparation requires weeks reconstructing past state from incomplete records
Cannot prove continuous adherence to controls, only point-in-time snapshots
Siloed point solutions: Automated collection with manual aggregation
Compliance tools automate evidence collection within their scope but IT must stitch reporting together.
Key characteristics:
Automated evidence collection within each tool's domain
Scheduled compliance checks per system
Manual aggregation required for cross-system compliance requirements
Each platform generating its own audit logs and reports
System limitations:
Compliance reporting still requires manual coordination across multiple tools
Cross-system security controls lack unified verification
Gap analysis requires comparing data from disparate sources
Audit preparation overhead reduces but remains significant
End-to-end automation: Policies as compliance controls
Security policies and compliance controls converge, such that enforcement generates its own evidence automatically.
Key characteristics:
Policies function as compliance controls with automated enforcement
Continuous, adaptive enforcement based on role, location, and device status
Automated evidence generation across all apps and devices
Real-time audit readiness without preparation fire drills
Technical transition:
Security policies simultaneously function as compliance controls
Policy enforcement automatically generates audit evidence in real-time across all systems
Compliance reporting shifts from periodic reconstruction to continuous queryable state
Organizations achieving end-to-end automation consolidate manual compliance processes and disconnected monitoring tools onto a single platform where enforced policies automatically generate audit evidence. Compliance requirements translate directly into automated controls that document their own enforcement continuously, eliminating both the periodic evidence gathering of manual approaches and the multi-system correlation required when using point solutions.
End-user experience
End-user experience maturity measures the coupling between users and IT staff for routine operations.
Manual: Tight coupling with high latency
Every user request requires IT staff intervention with manual coordination and execution.
Key characteristics:
Ticket-based request system with human approval and execution
Synchronous operations dependent on IT staff availability
No programmatic API for common user operations
Manual password resets, access requests, and software installations
System limitations:
Common operations exhibit high latency (hours to days)
Routine user requests – password resets, access permissions, software installations – consume substantial IT capacity
Support request volume scales linearly with user count, creating unsustainable IT workload
Siloed point solutions: Fractured self-service
Self-service portals exist but users must navigate multiple disconnected interfaces.
Key characteristics:
Self-service capabilities within individual platforms
Different UX patterns across tools
Some automation but fragmented across systems
Manual coordination still required for cross-system requests
System limitations:
Users must learn multiple self-service systems with different interfaces and capabilities
Cross-system requests still require IT coordination
Inconsistent user experience results in confusion and reduced self-service adoption
End-to-end automation: Unified, contextual experience
Seamless experience across devices and applications with intelligent self-service integrated into automated workflows.
Key characteristics:
Consistent interface across all systems
Context-aware self-service that understands user role and permissions
Automated workflows eliminating IT intervention for routine operations
Intelligent routing for complex requests requiring approval
Advancing to end-to-end automation replaces fragmented self-service portals and manual ticketing systems with a single interface built on shared user and device data. This consolidation enables context-aware self-service that understands user roles and permissions across all systems, eliminating both the manual coordination of the current state and the disjointed user experience created by multiple point solutions.
Ready for end-to-end automation? Get Rippling IT
For IT teams looking to move beyond manual processes and fragmented point solutions, Rippling's unified workforce platform manages identity, devices, access, and compliance in one place, eliminating the integration overhead and coordination gaps that slow down too many IT teams today.
With Rippling, teams can consolidate their siloed tools onto a single platform with a shared data layer. Onboard new employees with automated provisioning across all apps and devices, enforce security policies that adapt in real-time based on role and device status, and maintain continuous audit readiness, all from one intuitive interface. Advanced workflows and context-aware policies let you automate end-to-end operations while maintaining 360° visibility.
By eliminating the middleware, synchronization scripts, and manual coordination required when identity providers, MDM platforms, and provisioning tools operate independently, Rippling frees your team from operational firefighting to focus on the strategic initiatives that drive your business' growth.
Disclaimer
Rippling and its affiliates do not provide tax, accounting, or legal advice. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for tax, legal, or accounting advice. You should consult your own tax, legal, and accounting advisors before engaging in any related activities or transactions.
Rippling editorial policy: Rippling puts our customers (and prospective customers!) first. The Rippling team is committed to providing information supported by product data, expert insights, and real customer feedback to inform all of our content. All of our content is reviewed by product experts for accuracy and freshness.
Hubs
Author
The Rippling Team
Global HR, IT, and Finance know-how directly from the Rippling team.
Explore more
See Rippling in action
Increase savings, automate busy work, and make better decisions by managing HR, IT, and Finance in one place.


























































































![[Blog – Hero Image] Identity management](http://images.ctfassets.net/k0itp0ir7ty4/5Hsu8HkmyPFWqWKMcgpz2z/d9c5dad0dae54b424f8977ee85388ae4/Header_Identity_Management_Software_02.jpg)
![[Blog - Hero Image] IT onboarding](http://images.ctfassets.net/k0itp0ir7ty4/4tojGXxBbkIaeQMNEJUNV8/92acd5c6769ed7dffa1201f3f07a3181/Header_IT_Onboarding.jpg)
